Notre site dispose désormais d'un mode éco. N'hésitez pas à l'essayer !
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a testing technique used to compare the performance of two versions of a marketing element, such as a landing page, an advertisement, or an email marketing campaign.
The goal of A/B testing is to determine which of the two versions performs better in terms of conversion rate, click-through rate, or other key performance indicators. The idea is to make decisions based on objective data rather than guesses or assumptions, while also improving the performance of your marketing campaigns and maximizing the return on investment (ROI) of your efforts. Finally, it can also help you understand your users' preferences and behaviors, which can be useful for improving the products and services you offer.
To set up an A/B test, you first need to create two versions of the marketing element you want to test. For example, if you want to test a landing page, you will need to create two different versions of that page, modifying one or more elements such as the headline, images, text, or calls-to-action.
Once both versions are ready, you can launch the test by directing a representative sample of your audience to each version. During the test, you can track the performance of the two versions using analytics and tracking tools to measure indicators such as conversion rate, click-through rate, or time spent on the page.
There are several approaches to setting up a test, including redirect testing, A/B testing, and multivariate testing. The choice of approach depends on the situation and the goals of the test, as well as the resources and skills available.
To conclude this first part, here is a “simple” and visual representation of a possible A/B test on your site.
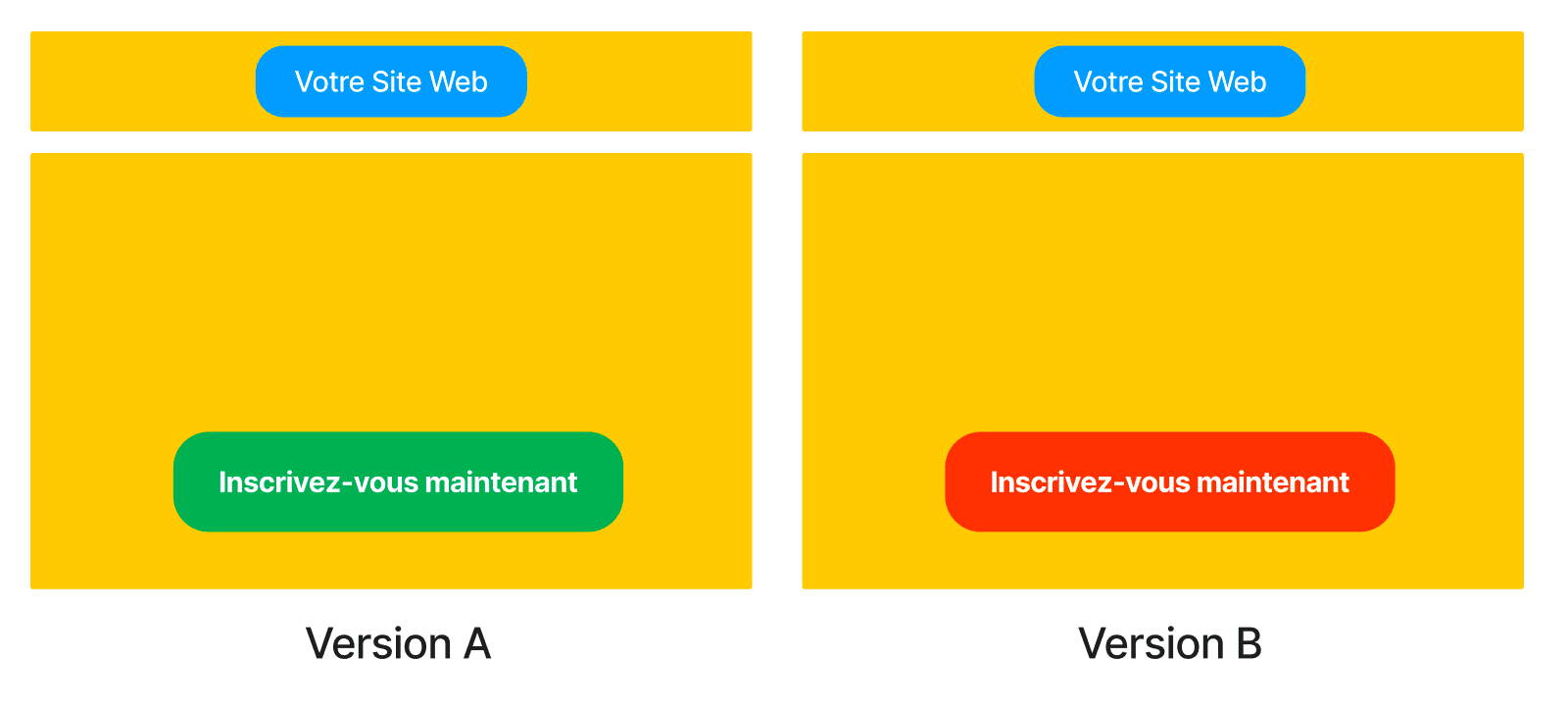
Here are some benefits you can gain from A/B testing:
The choice of approach depends on the situation and the goals of the test, as well as the resources and skills available. It is important to choose the approach that best suits each situation to achieve the best possible results.
Bias is any factor that can influence the behavior of the studied population sample. This can include differences in traffic sources, devices, time of day, socio-demographic characteristics, and any other element that causes a lack of uniformity in the population seeing different versions of a page. Bias can significantly impact the results of a study or experiment, and it is important to account for it to obtain accurate and reliable results.
Many biases can affect the results of a study or experiment, including the representativeness of the sample population. For example, if you present a different version of a page to mobile users and desktop users, you may act based on assumptions about the characteristics of each group. However, this can be problematic as it ignores the impact that the context of a user can have on their behavior. For example, a person may not make the same purchases on their personal computer as on their phone while commuting.
But the most important and potentially dangerous bias concerns not the observed population but the observer themselves. We have all found ourselves working on a homepage thinking it would be a success, only to launch it and see little or no engagement. This can be frustrating, but it is also a reminder that the real problem of representativeness in testing is the risk of observer bias. It is important to remain objective and avoid making assumptions about the success of a page or experiment based on our personal beliefs or prejudices.
It is important to consider contextual biases when conducting experiments or analyzing data. However, it can be even worse to rely on weak statistics to draw meaningful conclusions. This is where the concept of statistical significance comes into play.
In statistics, the result of a study on a sample population is considered statistically significant when it is unlikely to be due to factors such as an incorrect or non-representative sample (Bayesian inference). This reliability is generally determined by examining values, differences in values, or relationships between values and determining if they are high or low enough to be considered significant. In general, we aim for a 95% reliability before making a decision. We interpret these 95% as meaning that there is a 95% chance that version A is indeed more effective than version B in our test.
There are many tools for A/B testing, some paid (with a free trial period, depending), such as Optimizely, VWO, A/B Tasty, and many others. (Make sure to check the incoming volume on your site as prices can rise quickly, and it is sometimes difficult to justify such tools/tests when the volume is insufficient, which is often the case in low-volume countries like Luxembourg.)
Now that you know a bit more about A/B testing and its various possibilities, all that remains is to implement it in your strategy.